Portique vs grue à portique : 6 avantages clés pour vous aider à choisir la meilleure option
Table des matières
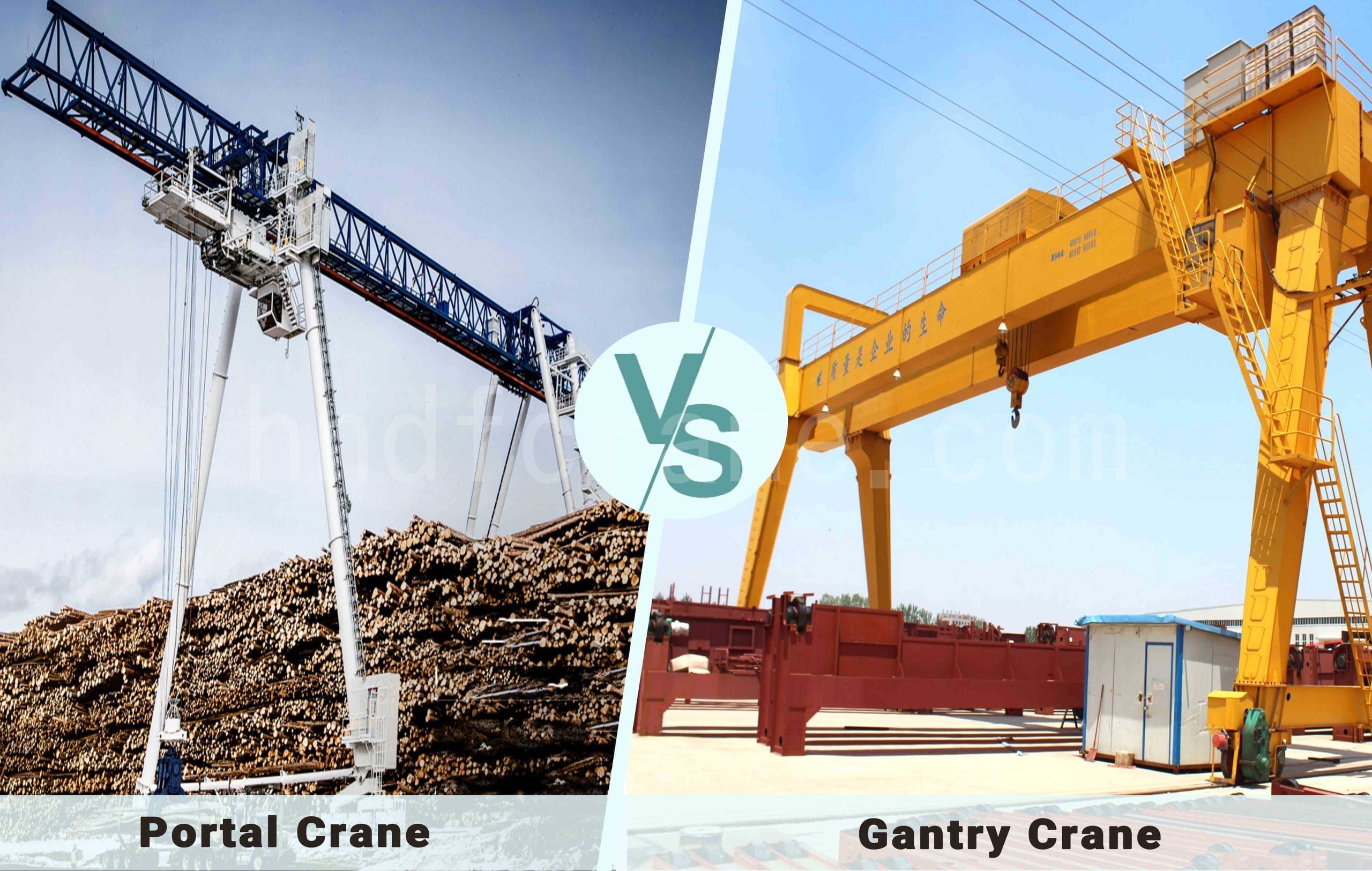

Lors du choix d'un équipement de levage, il est essentiel de comprendre les différences entre les différents types de grues. Les grues portiques et les grues à portique sont deux types courants, chacun avec des conceptions et des applications uniques. Mais qu'est-ce qui les distingue exactement ? Laquelle est la mieux adaptée à vos besoins ? Dans cet article, nous explorerons les caractéristiques, les avantages et les inconvénients des grues portiques et des grues à portique pour vous aider à faire le meilleur choix.
1. Comparaison des informations de base
Définition de portique:
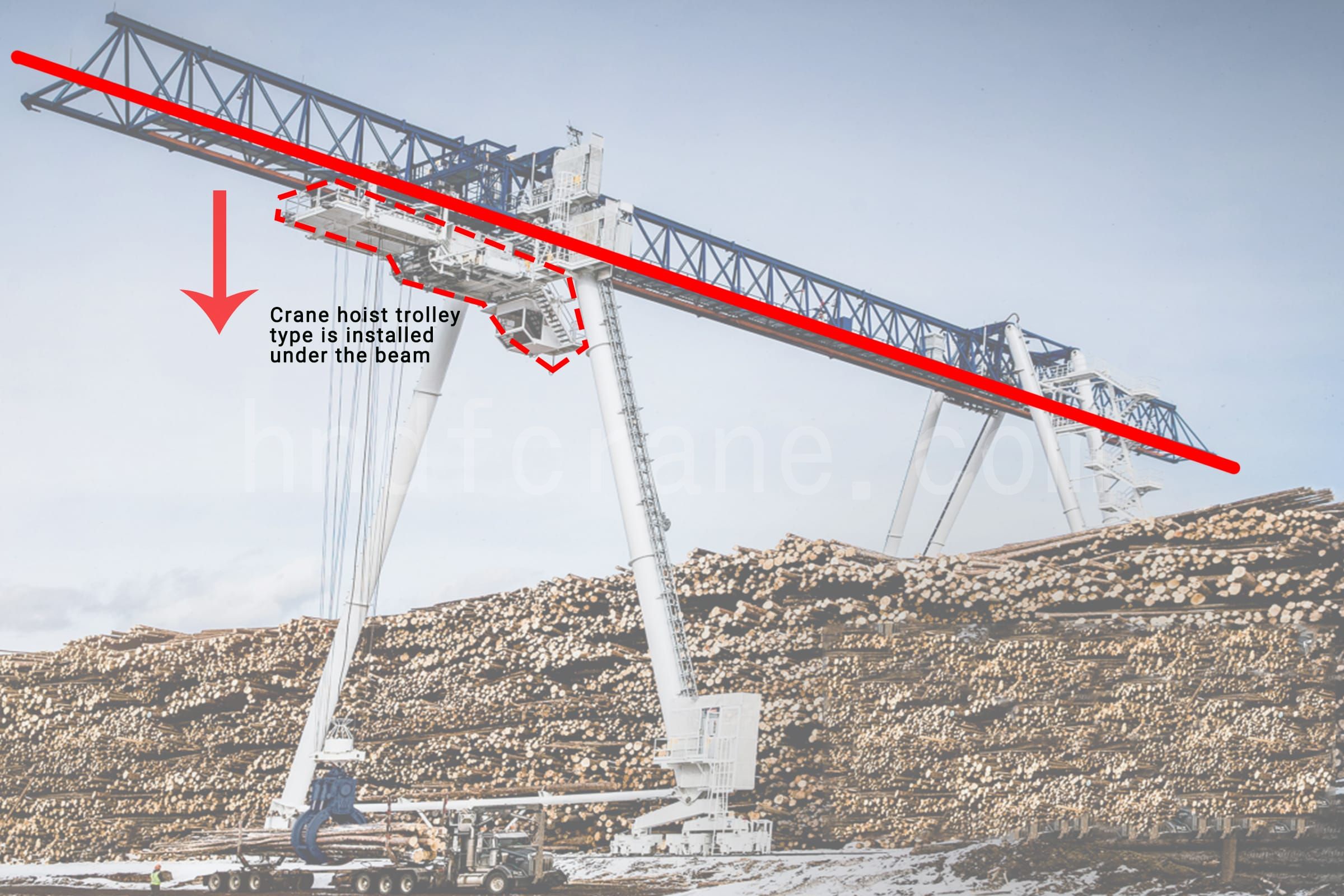
- Conçu pour les longs trajets, il peut être tourné à 360° en orbite.
- Souvent utilisé pour l'empilage de bois dans les parcs à bois et l'empilage de stockage dans les parcs à bois.
- La grue portique assure le déchargement et le stockage du bois, ainsi que l'alimentation du bois, le tout dans une seule unité. Elle peut effectuer jusqu'à 40 ramassages par heure (si la distance de déplacement est minimale). De cette façon, plusieurs camions peuvent être déchargés si nécessaire. Vous pouvez saisir un camion chargé de piquets bruts à la fois.
Portique industriel applicable:
- Pour les applications et environnements exigeants dans les secteurs des produits forestiers, de l'intermodalité, de la biomasse/des granulés, du béton et de nombreuses autres industries, les grues portiques doivent être construites de manière robuste.
Avantage du portique :
- Sûr, intelligent et efficace
- L'énergie est économisée, la puissance est augmentée, le freinage régénératif est utilisé et à chaque mouvement descendant ou décélération, l'énergie est renvoyée au réseau au lieu d'être dissipée par la résistance. Avec plus d'énergie renvoyée au réseau, moins d'énergie doit être produite, ce qui augmente les économies de coûts.
- La cabine du conducteur est ergonomique et lorsque les travailleurs se sentent à l'aise, ils sont plus susceptibles de se concentrer sur la tâche à accomplir, réduisant ainsi le risque d'accidents ou de blessures.
- Adoptez une technologie intelligente.
- Augmentation de la surface de stockage.
- La grue à portique occupe seulement 4% de l'espace de la cour
- Le portique permet également un stockage vertical jusqu'à 22,86 m, augmentant considérablement la capacité cubique de stockage du dépôt.
- La grue portique est équipée de freins anti-tempête et peut fonctionner dans toutes les conditions météorologiques, même dans les zones à vents forts.
- La grue portique s'adapte aux mouvements le long de la piste, ce qui permet à la grue et à la piste de rester en bon état sur le long terme.
Définition de grue à portique :
- La portée est généralement de 35 m, adaptée à un usage général.
Secteurs d'application des grues à portique :
- Gare de marchandises, chantier de construction, gare de transfert ferroviaire
- Chantiers navals et ports
- Usine de poutres
Avantage du portique :
- Taux d'utilisation élevé, large utilisation, forte adaptabilité, forte polyvalence, c'est l'équipement de levage de portail le plus couramment utilisé, poids nominal de 5t à 500t.
- La grue à portique occupe 25% de la surface du chantier.
Portique de grue

Grue à portique
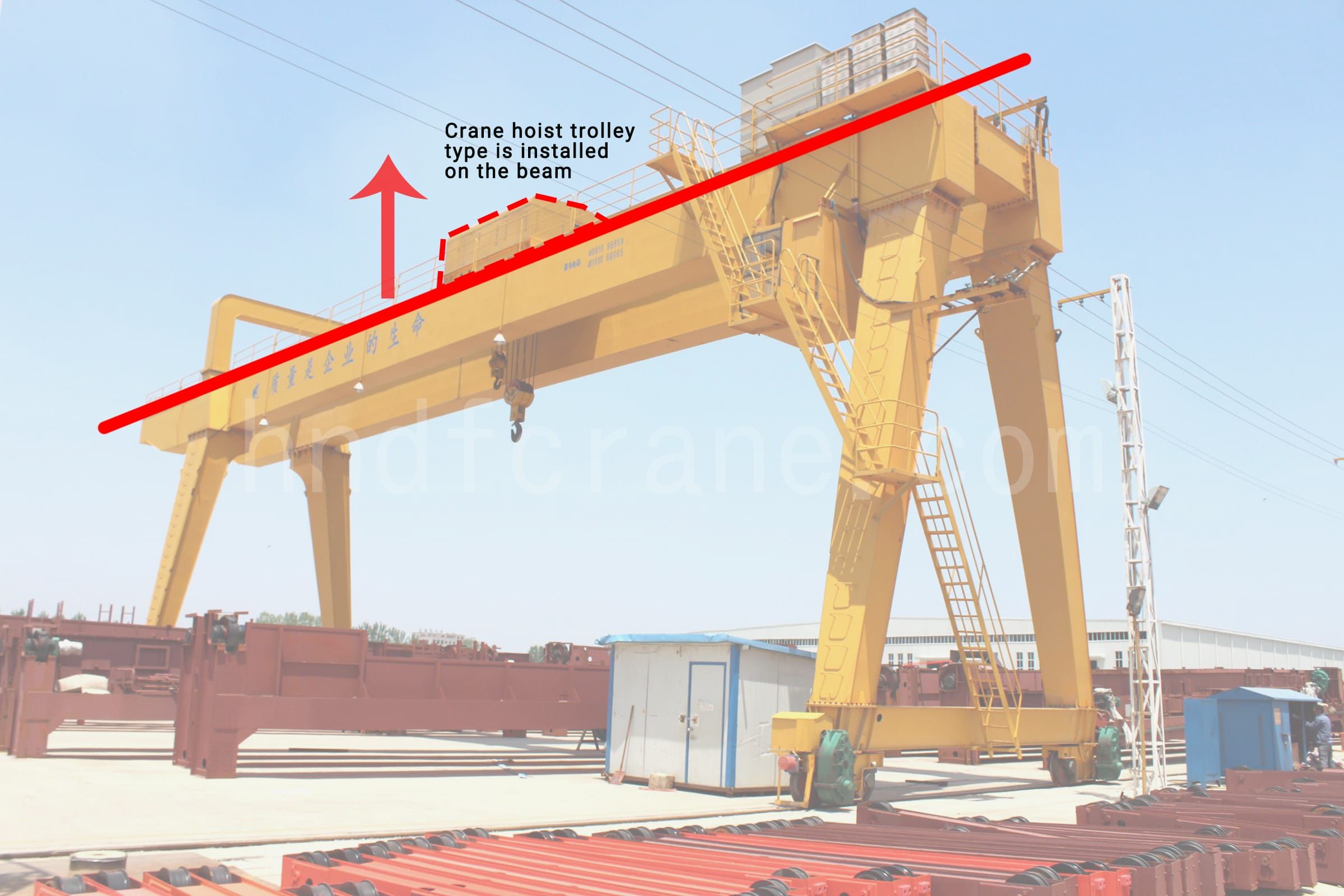

2.Comparaison de classification
Portique de grue
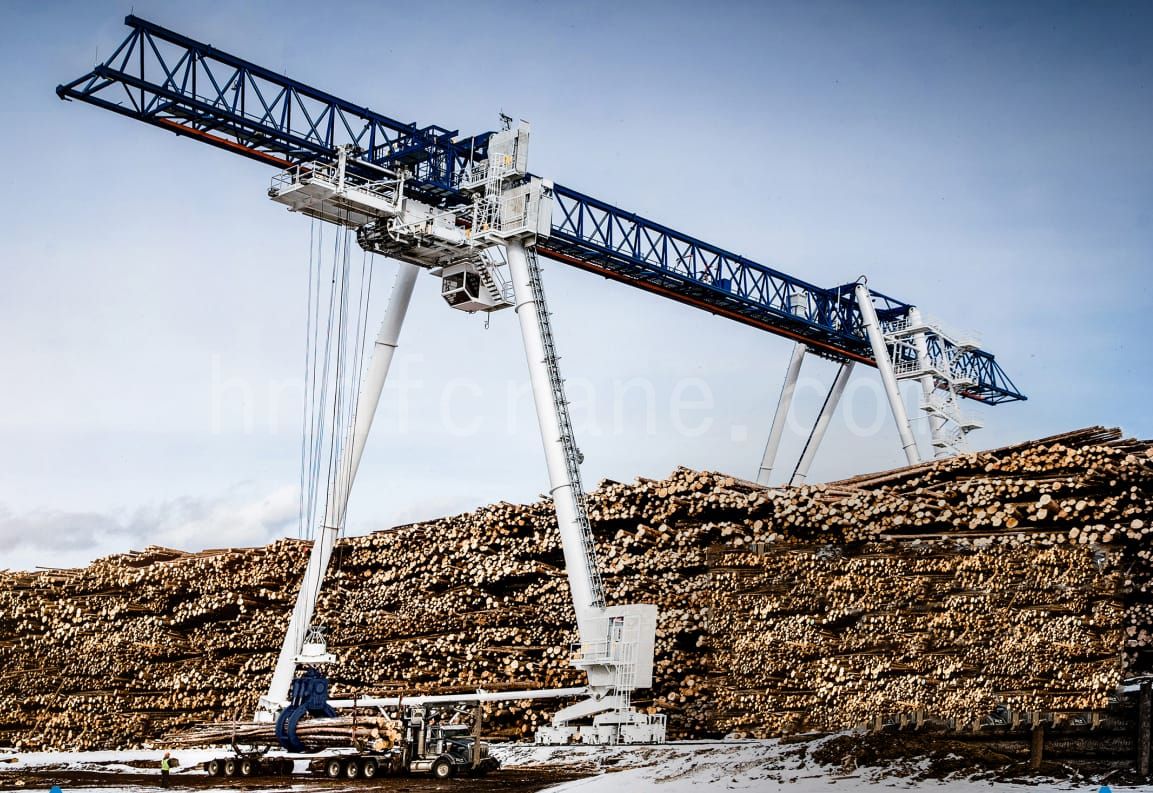

Portiques à voie droite
- Le plus populaire et le plus optimal pour les futures extensions de pistes et l'agrandissement de l'espace de stockage.
- Assure un flux de circulation optimal des camions et un stockage maximal.

Portiques rotatifs
- S'adapte souvent aux endroits où les grues à voie droite ne s'adaptent pas.
- Fournit un espace de rangement à l'intérieur et à l'extérieur du rail.
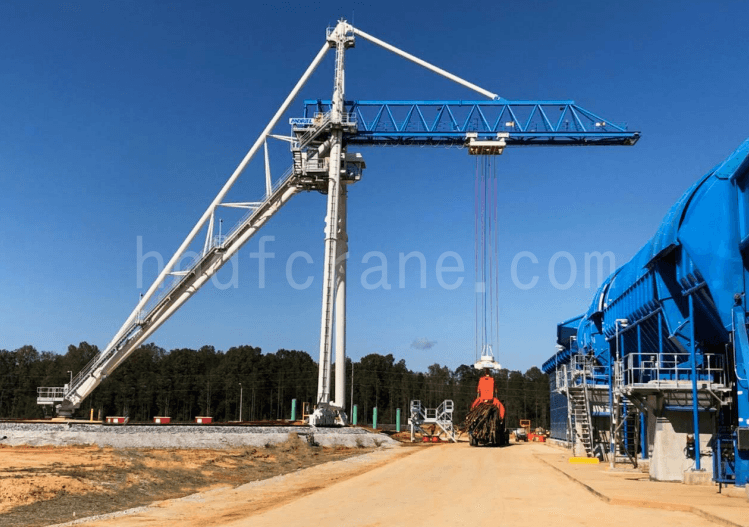

Grues à flèche pour grumes
- La grue tourne autour du support central du palier. Les deux grands pieds avant se déplacent sur une piste circulaire, ce qui permet à la grue d'empiler les grumes pour les stocker jusqu'à ce qu'elles doivent être introduites dans la trémie.
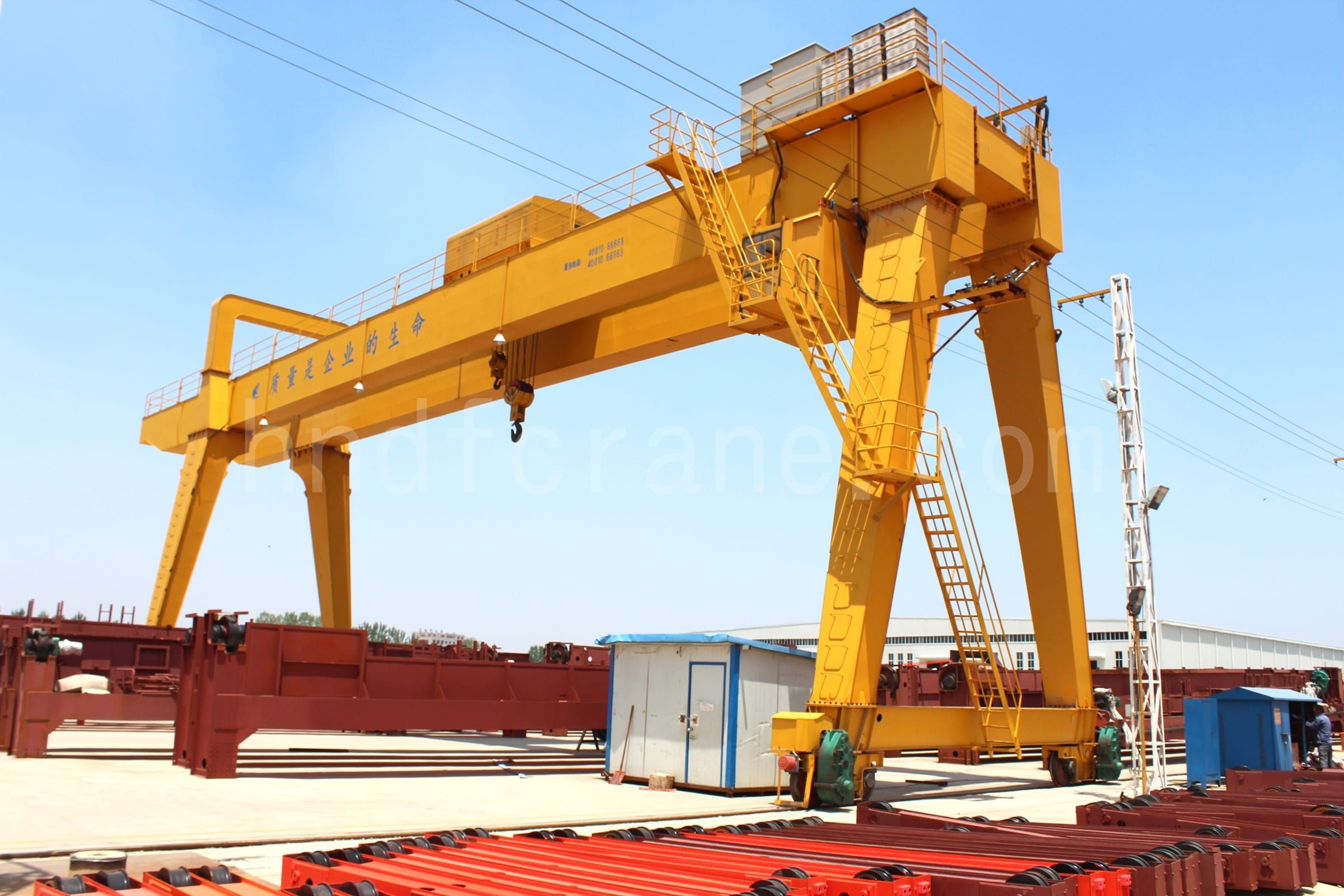
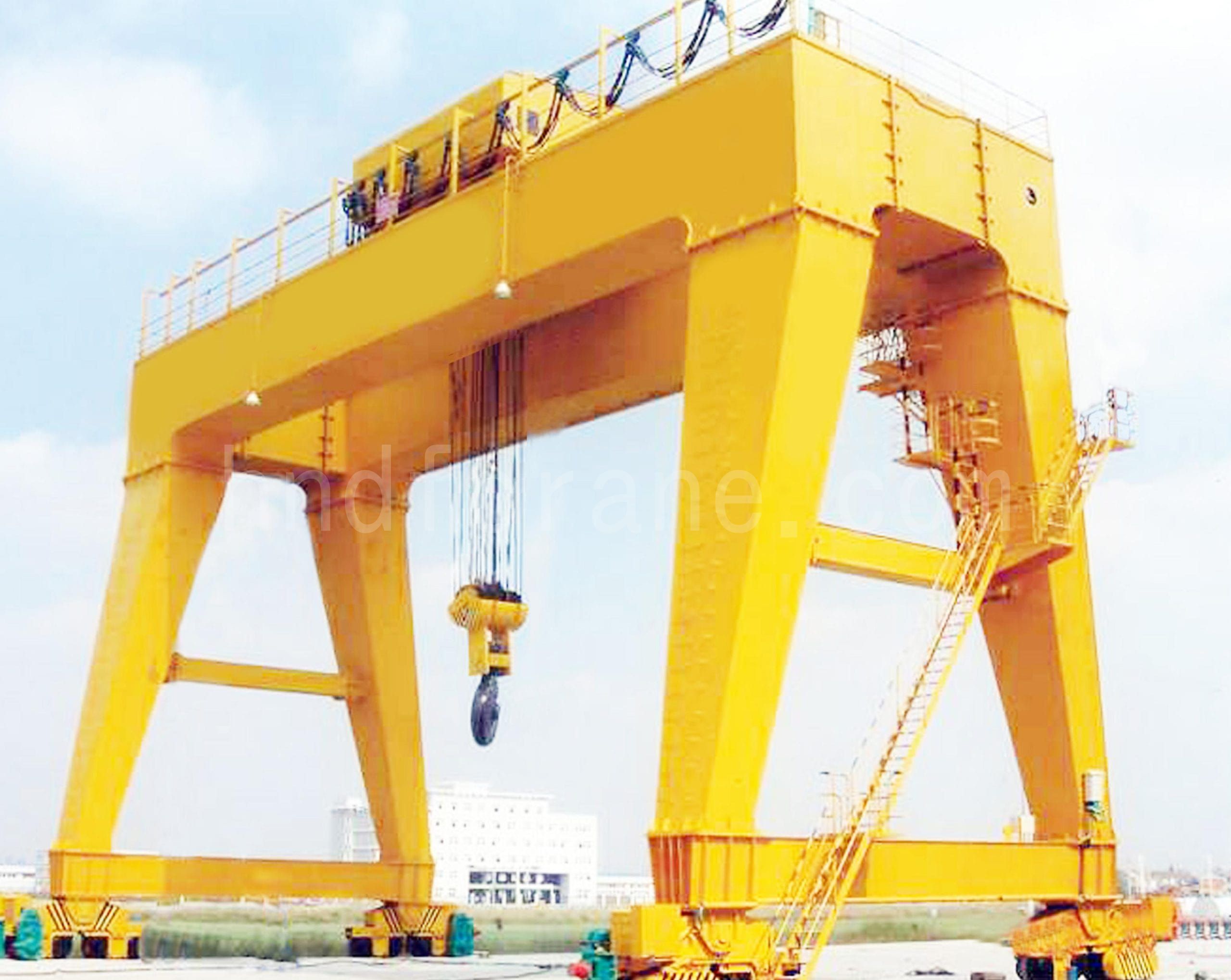
Grue à portique

Cadre de porte extérieur à double cadre en porte-à-faux

Cadre de porte simple face avec cadre extérieur en porte-à-faux

Pas de cadre en porte-à-faux externe
Traditionnel grues à portique est largement applicable, et il existe de nombreuses formes et classifications, dans cette catégorie, les trois types ci-dessus peuvent également être fabriqués en portiques à treillis, Dafang Crane peut personnaliser les produits dont vous avez besoin un à un. Vous pouvez nous contacter si vous avez besoin de quoi que ce soit.
3. Comparaison des coûts
L'investissement initial de la grue Poral est généralement inférieur à celui du portique traditionnel car le portique est plus léger et capable de fonctionner sur des voies qui ne nécessitent pas les mêmes exigences de parallélisme et de rectitude.
La grue à portique ne nécessite que des rails standards posés sur des traverses de chemin de fer sur un lit de gravier ou une simple fondation en béton. Elle s'adapte aux terrains instables, limitant ainsi le besoin de travaux de surface coûteux tout en permettant aux grues de fonctionner à pleine capacité partout où des rails peuvent être posés. Ce type d'installation permet d'économiser beaucoup d'argent par rapport aux fondations profondes et lourdes d'une grue à portique traditionnelle.
Économies de coûts d'exploitation, la grue à portique combine le déchargement, le transport et l'empilage des matériaux en une seule opération efficace. La combinaison de ces activités réduit les besoins en équipements, en maintenance et en personnel, réduisant ainsi considérablement les coûts d'exploitation par rapport aux chantiers utilisant une grue à portique.
La grue Poral est équipée de moteurs et de commandes économes en énergie conçus pour un fonctionnement fiable à long terme sans entretien majeur et sans coûts associés.
4. La différence entre les structures à poutres-caissons et les structures à treillis

- Cette conception en treillis est rentable par rapport à structures à poutres-caissons. La conception ouverte permet également une inspection facile des soudures critiques tout au long de la durée de vie de la grue.
- La poutre en treillis est la poutre principale avec le matériau opposé (tel que l'acier canalisé, l'acier d'angle, l'acier en T), qui peut ajuster l'angle et la longueur, et est plus propice à la manipulation d'objets irréguliers.
- Cette structure peut réduire la zone au vent de la grue, une forte résistance au vent, adaptée à une utilisation dans des endroits ouverts et venteux.
- La conception ouverte permet également une inspection facile des soudures critiques tout au long de la durée de vie de la grue.
- En raison de la conception ouverte de la structure de la poutre principale en treillis, la révision et l'entretien sont relativement simples, en particulier pour certaines structures trop petites, qui peuvent être mieux observées et réduire la zone aveugle dans le processus de maintenance.
- La structure de poutre principale en treillis offre une plus grande liberté de structure des jambes, une meilleure adaptabilité et une meilleure flexibilité.
- La structure de poutre principale en treillis est plus facile à démonter grâce à sa structure de jambe amovible.

- La grue à portique avec structure en caisson présente une faible résistance au vent, une auto-charge et un coût plus élevé que le type à treillis.
- La poutre-caisson du portique est constituée d'une plaque d'acier soudée dans une structure en caisson.
- La grue à portique de la structure de type boîte est complètement fermée et ne peut pas observer et inspecter directement sa structure mécanique interne.
- La grue à portique de type caisson présente une bonne stabilité structurelle, ce qui permet de mieux maintenir la sécurité et la fiabilité du fonctionnement de l'équipement.
- La grue portique à structure en caisson a une durée de vie plus longue grâce à sa bonne résistance à la fatigue.
- La grue à portique de structure de type boîte doit disposer de certaines installations et conditions matérielles sur le site d'utilisation avant de pouvoir être démontée.
Références: 大跨度门式起重机刚性支腿对结构刚度的影响分析
5. La différence entre les pieds flexibles et les pieds articulés
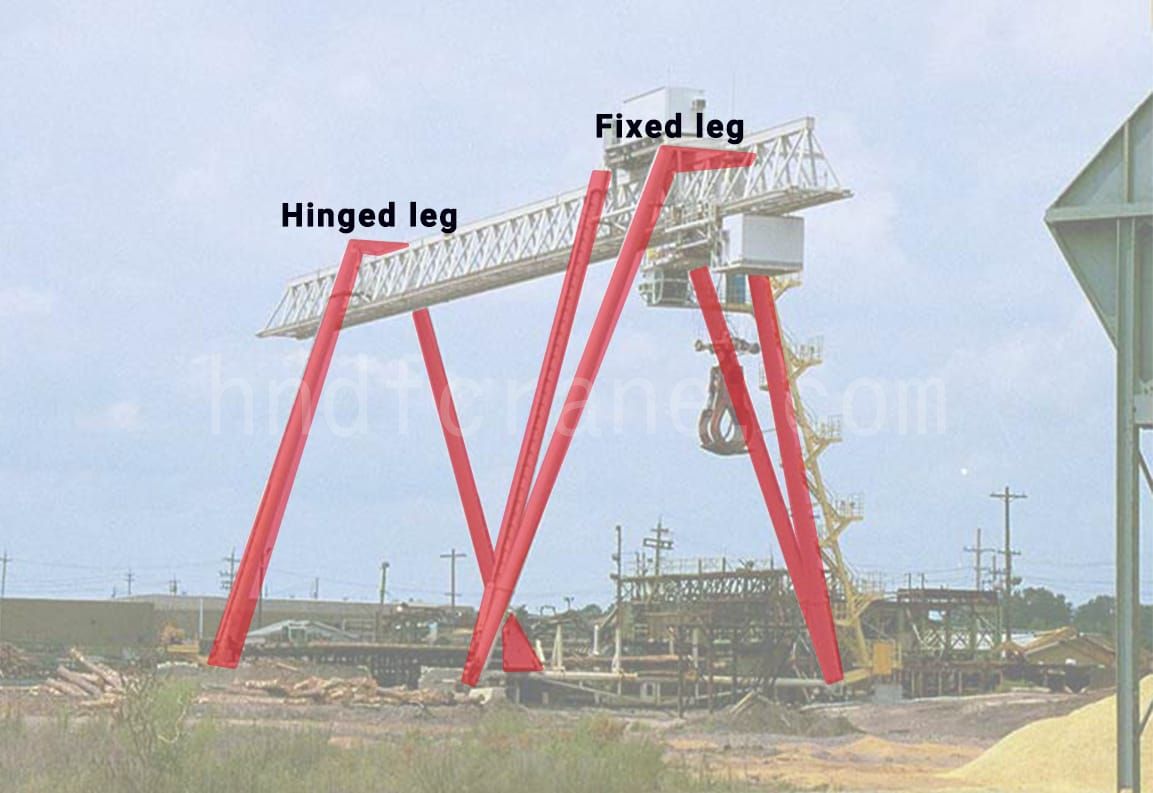

- La grue à portique est conçue pour une flexibilité maximale, réduisant au minimum l'entretien des structures et des voies. La grue à portique est conçue pour une flexibilité maximale, réduisant au minimum l'entretien des structures et des voies.
- Les pieds flexibles ont un certain degré de liberté et sont articulés lorsqu'ils sont connectés à la poutre principale.
- Les pieds flexibles sont soudés avec deux tubes en acier d'épaisseur de paroi égale, et le fond est relié à la poutre inférieure dans une structure triangulaire avec une bonne stabilité.
- Étant donné que les pieds flexibles peuvent être déplacés le long de la piste annulaire de la grue, ils conviennent à certains endroits où la grue doit effectuer des travaux courbes.
- Il est plus inclusif pour la fondation et peut être appliqué sur un sol irrégulier.
- Les pieds flexibles conviennent également aux opérations qui nécessitent que la grue s'approche ou traverse d'autres structures.
- Faible capacité de charge.
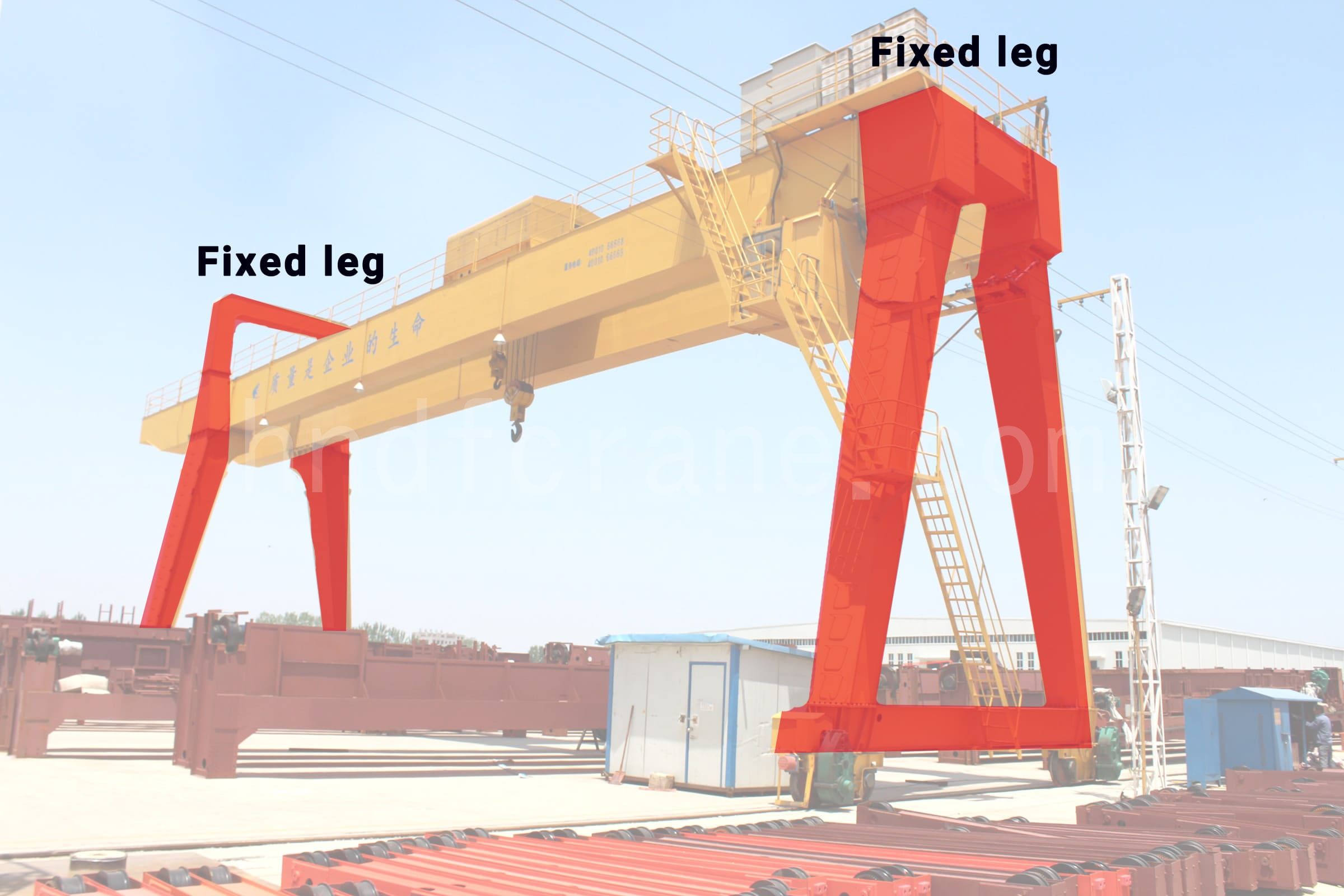
- Les pieds rigides sont boulonnés lorsqu'ils sont connectés à la poutre principale, de sorte que le degré de liberté est entièrement limité
- La jambe rigide est également une structure de type boîte et sa section transversale diminue de haut en bas.
- En raison de la forte capacité portante et de la stabilité du pied rigide, il convient à certains endroits où la grue doit effectuer des opérations à charge élevée et de haute précision.
- Les jambes rigides supportent de nombreux équipements de la grue, tels que les salles de contrôle électrique, les résistances, etc. Afin de faciliter l'accès du personnel à la cabine de conduite ou à la poutre principale, un escalator est installé entre les deux jambes rigides.
- Les pieds rigides conviennent également à une large gamme d'opérations, telles que l'exploitation minière et la manutention dans les mines à ciel ouvert, les grands parcs de stockage, etc.
- Coûts d'entretien élevés et exigences élevées pour les fondations
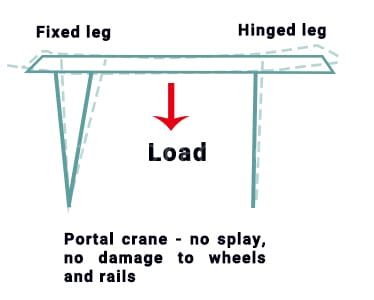
- La grue à portique adopte une conception de jambe rigide et flexible. Cette conception rigide et flexible permet aux jambes de tourner librement par rapport à la poutre principale, ce qui peut réduire le phénomène de concentration de contrainte causé par le fonctionnement de déflexion de la grue à portique ou la dilatation thermique de la poutre principale
- Les portiques des deux côtés adoptent généralement la forme d'un pied rigide et d'un pied flexible. Un pied du portique est articulé avec le pont, de sorte que l'ensemble du portique est un système statiquement déterminé, ce qui élimine la poussée latérale du wagon sur la voie causée par la charge de levage. En même temps, l'état de contrainte du système de portique statiquement déterminé est relativement clair lorsque le wagon se déplace de travers.
- Cependant, ce type de structure présente une faible rigidité structurelle, de mauvaises caractéristiques dynamiques, un déplacement latéral important généré par la poutre principale lors du levage et une rigidité dynamique horizontale verticale insuffisante.
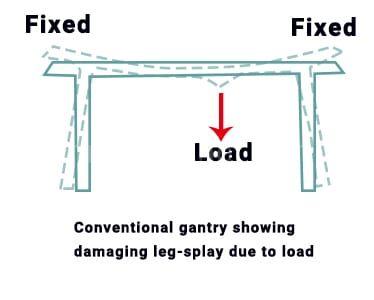
- Le chariot entièrement chargé de la grue à portique est situé au centre de la poutre principale. En raison de la désynchronisation du chariot sous les pieds des deux côtés, le cadre du portique sera tordu et des accidents graves se produiront, entraînant des conséquences désastreuses.
- Les structures rigides, telles que les ponts roulants à poutres-caissons, sont extrêmement sensibles aux charges latérales causées par la déflexion des jambes, ce qui entraîne l'usure des boudins de roue et le remplacement éventuel des voies.
- La grue à portique adopte une structure à double jambe rigide avec une rigidité élevée et de bonnes caractéristiques dynamiques. Cependant, en raison de sa structure statique indéfinie, la partie inférieure de la jambe se décalera vers l'extérieur lors de la charge de levage. Si le décalage dépasse l'écart entre la roue et la voie (dans des circonstances normales : l'écart entre la roue et la voie ne dépasse pas 15 mm, la grue ne rencontrera pas de problèmes dangereux), alors le chariot produira une poussée latérale importante sur la voie, la force sera défavorable au fonctionnement du chariot et provoquera le phénomène de rongement du rail. Dans le même temps, les exigences en matière de fixation du rail sont plus élevées, en particulier lorsque la portée est grande, même l'état sans charge apparaîtra également un phénomène de rongement du rail.
6. Comparaison des bases de grue
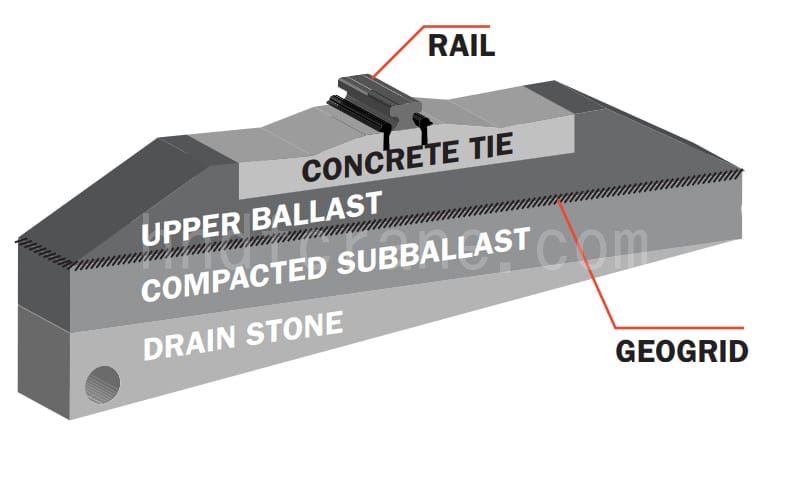
- L'image montre un schéma en coupe transversale d'une fondation de piste de type « traverse et ballast », qui est utilisée pour soutenir la grue. La fondation est construite avec plusieurs couches, chacune ayant une fonction distincte pour assurer la stabilité, la durabilité et un drainage adéquat. Voici une répartition des couches du bas vers le haut :
- Pierre de drainage:Il s'agit de la couche la plus basse, constituée de pierres destinées à assurer un drainage adéquat. Cette couche permet d'éviter que l'eau ne s'accumule sous la fondation, ce qui pourrait entraîner son affaiblissement ou son érosion.
- Sous-ballast compacté:Au-dessus de la couche de pierre drainante se trouve le sous-ballast compacté. Cette couche est généralement constituée de matériaux plus fins et est compactée pour fournir une base stable aux couches supérieures. Elle permet de répartir la charge des couches supérieures de manière plus uniforme et ajoute une capacité de drainage supplémentaire.
- Géogrille:Une géogrille est placée au-dessus du sous-ballast compacté. Les géogrilles sont des matériaux géosynthétiques utilisés pour renforcer le sol, offrant une stabilité et une résistance supplémentaires à la fondation. Elles empêchent le mouvement du sous-ballast et augmentent la capacité portante globale de la fondation.
- Ballast supérieur:Cette couche est constituée de pierres plus grosses ou de ballast qui fournissent une base solide aux traverses en béton. Le ballast est essentiel pour répartir les charges des rails et des traverses et pour maintenir l'alignement de la voie en résistant aux forces latérales, longitudinales et verticales.
- Lien en béton:Les traverses en béton sont placées sur la couche supérieure du ballast. Ces traverses sont des éléments essentiels qui maintiennent les rails en place, préservant ainsi l'écartement et l'alignement des voies.
- Rail:Enfin, le rail est posé sur les traverses en béton. Les rails sont les rails sur lesquels se déplacent les grues. Ils sont fixés aux traverses en béton à l'aide de clips ou d'autres éléments de fixation pour les maintenir solidement en place.
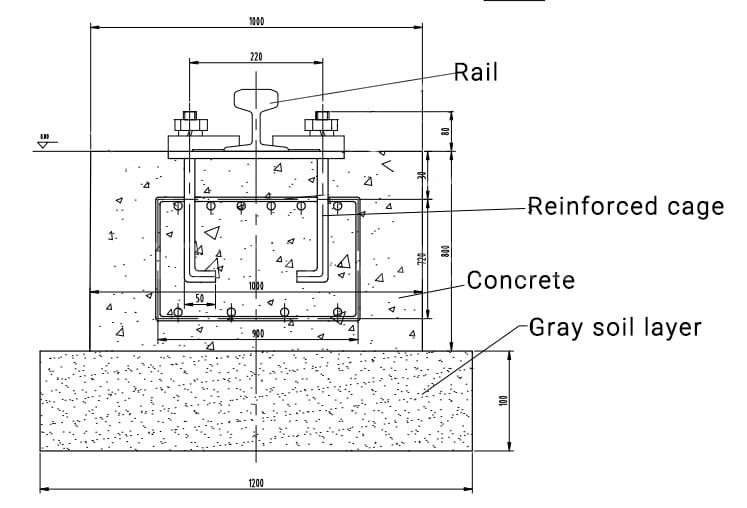
- L'image fournie montre un dessin technique d'une conception de fondation pour un système de voies ferrées. Elle détaille la section transversale de la fondation, mettant en évidence les couches et les composants utilisés dans sa construction. Voici une répartition des éléments représentés sur le dessin :
- Rail:Il s'agit de l'élément le plus élevé de la fondation. Le rail est la voie métallique sur laquelle se déplacent les trains ou les grues. Il est généralement fabriqué en acier à haute résistance et est fixé à la fondation en béton à l'aide de boulons et d'éléments de fixation. Le rail illustré est monté directement sur la surface en béton.
- Cage renforcée:Sous le rail, encastré dans le béton, se trouve une cage en acier renforcé. Cette cage est composée de barres d'armature en acier disposées en forme de grille, ce qui assure la résistance à la traction et améliore l'intégrité structurelle globale du béton. La cage renforcée empêche les fissures et répartit les charges de manière plus uniforme dans le béton.
- Béton:La couche de béton constitue le corps principal de la fondation. Il s'agit d'un bloc solide et renforcé qui soutient le rail et absorbe les charges transférées par le rail. Le béton est coulé sur la cage en acier renforcé et est conçu pour supporter des forces de compression importantes. Le dessin indique une épaisseur de 900 mm pour la fondation en béton, offrant une stabilité et un soutien substantiels.
- Couche de sol gris:La couche de sol gris est la base sur laquelle repose toute la fondation. Cette couche est probablement composée de sol compacté ou d'une sous-couche préparée qui fournit une base stable pour la fondation en béton. Le dessin montre que cette couche a une épaisseur de 100 mm, ce qui indique qu'elle est bien compactée et sert de base pour répartir la charge de la fondation en béton.
La grue portique ne nécessite que des rails standards posés sur des traverses de chemin de fer sur un lit de gravier ou une simple fondation en béton. Elle s'adapte aux terrains instables, limitant ainsi le besoin de travaux de surface coûteux tout en permettant aux grues de fonctionner à pleine capacité partout où des voies peuvent être posées. Ce type d'installation permet des économies importantes par rapport à la structure en acier de la grue portique ou à la fondation profonde et lourde d'une grue portique traditionnelle.
En résumé
Lorsque vous considérez les économies de taille de chantier, la réduction de la main-d'œuvre, les rotations plus rapides des camions, le nombre réduit de pièces d'équipement, la réduction de la maintenance, l'élimination de l'utilisation de mazout et de la contamination du sol, la grue à portique est la solution INTELLIGENTE.
En résumé, grâce à une compréhension approfondie des différences entre la grue à portique et la grue à portique sous cinq aspects : classification, coût, type de caisson et de treillis, pied rigide et pied flexible et fondation, nous pouvons mieux évaluer leurs avantages dans différents scénarios d'application. La grue à portique, avec sa grande flexibilité et adaptabilité, convient à une utilisation dans des environnements où l'espace est limité ou où diverses manutentions sont nécessaires, tandis que la grue à portique, avec sa capacité de charge supérieure et sa polyvalence, est idéale pour les tâches de levage lourdes. Au moment de prendre votre décision finale, vous pouvez choisir l'équipement de levage qui vous convient le mieux en fonction de vos besoins opérationnels spécifiques, de votre budget et des conditions du site.
Que vous recherchiez un contrôle précis et une polyvalence, ou une stabilité et une rentabilité, l'équipe d'experts de Dafang Crane peut vous fournir des conseils et des solutions personnalisés pour vous assurer de maximiser le retour sur investissement. Contactez-nous et laissez-nous vous aider à trouver la solution de grue parfaite pour améliorer votre efficacité opérationnelle !
Envoyez votre demande
- E-mail: sales@hndfcrane.com
- WhatsApp : +86-191 3738 6654
- Tél : +86-373-581 8299
- Télécopie : +86-373-215 7000
- Ajouter : district industriel de Changnao, ville de Xinxiang, province du Henan, Chine








































































